
DMR Exceedances Report Help
The DMR Exceedances Report presents detailed information about DMR exceedances violations under the Clean Water Act National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permit program for a single permit. Data are from the EPA national program database, ICIS-NPDES. For information about the NPDES permit program, see NPDES Homepage.
The report is organized into four sections. Descriptions of the data elements presented on the report are provided in the sections below:
Instructions
Print Report
Use the Print button at the top of the DMR Exceedances Report to generate a printer-friendly version of the report, optimized for US letter size paper (8.5" x 11").
Report Options
Select an Exceedance TypeThe radio buttons allow for the selection of either Effluent Limit Exceedances or Benchmark Limit Exceedances. The default exceedance type selected on the DMR Exceedances Search is Effluent Limit Exceedances.
Adjust Date Range
The default date range is the range selected on the DMR Exceedances Search. Click on the start or end date to use the calendar to change the month and year. Select "Apply Changes" to update the tables and charts on the report: Total Exceedance Counts, Exceedance Counts by Pollutant, and Exceedance Details.
Display records identified as potential outliers or data errors
Use the icon to toggle records on or off. The default "on" displays exceedance records flagged for further review as potential outliers. When the toggle is changed to off, records with blue flags are removed from the Exceedance Details table and the counts in the charts will exclude those records.
Interact with the Exceedance Counts Chart
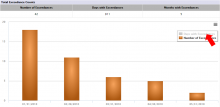
The chart provides a graphical representation of the counts of DMR exceedances during each monitoring period date. Hover your mouse pointer over any bar to view an attribute bubble containing the monitoring period end date, days with exceedances, and number of exceedances. See Total Exceedance Counts for descriptions of the data presented.
Click on a series label in the chart legend to hide or display the series. The vertical axis of the chart will dynamically adjust proportionate to the data displayed.
Data Dictionary
Facility Summary
Facility/permittee name and address are displayed at the top of the facility summary section.
Facility Information
NPDES ID: A unique 9-character ID assigned for each permit within the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) program. The ID may contain both letters and numbers and often begins with the two-letter abbreviation for the state in which the facility is permitted.
FRS ID: Facility Registry Service (FRS) identification number. FRS uniquely identifies a facility by assigning an identification number (FRS ID), and uses this FRS ID to link together all regulatory program database records (such as permit IDs and facility IDs that facilities use in reporting to EPA).
Other NPDES IDs associated with this FRS ID: Other NPDES ID linked to the primary NPDES ID within FRS. The DMR Exceedance Report displays information for one NPDES ID. Information for the associated NPDES IDs may be obtained by conducting a separate DMR Exceedances Search.
TRI ID(s): A unique 15-character ID assigned for each facility within the Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) program. The format is ZZZZZNNNNNSSSSS, where ZZZZZ = ZIP code, NNNNN = the first 5 consonants of the name, and SSSSS = the first 5 non-blank non-special characters in the street address.
CWNS ID: A unique identifier for a facility in the Clean Watershed Needs Survey. Most facilities identified are publicly owned treatment works (POTWs). Every four years, EPA and states conduct the survey to determine the capital needs for municipal wastewater treatment facilities to meet the goals in the Clean Water Act.
Major/Non-Major Indicator: A facility classification from the NPDES permitting authorities based on toxic pollutant potential, ratio of discharge flow/stream flow volume, conventional pollutant loading, public health impact, water quality factors, and proximity to coastal waters. EPA places greater priority on major facilities, and requires authorized states to prove more information about the compliance status of these dischargers. For more information, please see About the Data.
Facility Type: The facility ownership classification derived from codes in ICIS-NPDES. Facilities can be classified as publicly owned treatment works (POTW), non-POTW, federal, or state.
Latitude/Longitude: Displays the latitude and longitude of the facility or permit holder as maintained in ICIS-NPDES.
4-Digit SIC Code: The primary Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code in ICIS-NPDES. The SIC code describes the primary activity of the facility. The first two digits in the code define a major business sector; the last two digits denote a facility's specialty within the major sector. For more information, see the SIC Lookup.
6-Digit NAICS Code: Indicates the facility's or permit's primary North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Code. The NAICS Code has replaced the U.S. Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) system. The system was developed to give special attention to developing production-oriented classifications for (a) new and emerging industries, (b) service industries in general, and (c) industries engaged in the production of advanced technologies.
NAICS industries are identified by a 6-digit code. The first two digits represent the Industry sector, in which there exist 20 broad sectors. The third digit represents industry subsector, the fourth digit represents industry group, the fifth digit represents industry, and the sixth digit is U.S., Canadian, or Mexican National specific. For more information, see the NAICS Lookup.
Receiving Water Information
Water Body Name (from GNIS): The name of the water body from the Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) database in which the facility is permitted to discharge directly. A water body is a geographically defined portion of navigable waters, waters of the contiguous zone, and ocean waters under the jurisdiction of the United States, including segments of rivers, streams, lakes, wetlands, coastal waters and ocean waters.
Watershed Name and Number (12-Digit HUC): Name and corresponding 12-digit Hydrologic Unit Code (HUC), assigned by the US Geological Survey, used to classify watersheds in the United States and the Caribbean. The code consists of twelve digits which correspond to six levels of classification:
- Region (first-level, 2-digit HUC)
- Subregion (second-level, 4-digit HUC)
- Accounting unit (third-level, 6-digit HUC)
- Cataloguing unit (fourth-level, 8-digit HUC)
- Watershed (fifth-level, 10-digit HUC)
- Subwatershed (sixth-level, 12-digit HUC)
Listed for Impairment?: Displays "Y" if the water body in which the facility is located is listed for impairment.
Under section 303(d) of the CWA, states, territories, and authorized tribes are required to develop lists of impaired waters. These are waters that are too polluted or otherwise degraded to meet the water quality standards set by states, territories, or authorized tribes. The law requires that states establish priority rankings for waters on the lists and develop Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs), for these waters. A TMDL is a calculation of the maximum amount of a pollutant that a water body can receive and still safely meet water quality standards. For more information about impaired waters or TMDLs, please visit EPA's Overview of Impaired Waters and TMDLs Program.
Impairment Class: The impairment class or category of the water body in which the facility is permitted to discharge directly.
- 5. Impaired - TMDL needed. Available information indicates that at least one designated use is not being supported and a TMDL is needed (also known as the 303(d) listed waters).
- 4. Impaired - TMDL not needed. Available information indicates that at least one designated use is not being supported, but a TMDL is not needed (see subcategories).
- 4a. TMDL completed. A TMDL has been completed, but impairment still exists.
- 4b. TMDL alternative. Impairment is being addressed by a method other than a TMDL (e.g., stream bank improvements).
- 4c. Non-pollutant causes. Cause of impairment is not a pollutant (e.g., habitat destruction).
Detailed information on the categorization of waters can be found in Section V of the 2006 Integrated Report Guidance.
Permit Information
Permit Status: The Permit Status values reflect the stages in the permit life cycle.
- Effective - A permit that is in its lifetime (Effective Date <= current date < expiration date).
- Expired - A permit that 90 days after the expiration date has been reached on a permit that has no new Application Received Date or Complete Application Received date entered.
- Administratively Continued - A permit that is at the permit's expiration date. All monitoring data are still collected and used against the permit’s terms.
- Pending - A permit with incomplete data or a permit with an Effective Date that has not yet been reached.
- Retired - A permit that all monitoring data is stopped against a retired permit; used in conjunction with Reissue. If a Permit is reissued before its expiration date, the Permit Status Code or the previous version of the Permit will be set to Retired.
- Terminated - A permit that if the user enters the Termination Date, upon that date being reached, the system will automatically change the Permit Status Code to Terminated.
- Not Needed
Permit Issuance: The environmental agency that administers the permit, typically a state or EPA Region.
Original Issue Date: The first or oldest date in ICIS-NPDES in which the permit was issued.
Last Issue Date: The date the most recent permit in the selected date range was issued. Permits are typically reissued every five years.
Permit Effective Date: The date the most recent permit in the selected date range became effective.
Permit Expiration Date: The date the most recently issued permit in the selected date range expires.
DMR Signer: The name of the official that signed the DMR.
Approved Pretreatment Program?: A yes/no field to indicate a NPDES permit with an approved pretreatment program. A NPDES permit with pretreatment responsibilities prescribes for the reduction of the amount of pollutants, the elimination of pollutants, or the alteration of the nature of pollutant properties in wastewater prior to or in lieu of discharging or otherwise introducing such pollutants into a publicly owned treatment works [40 CFR 403.3(q)]. For more information, see NPDES Pretreatment.
Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Outfall: A yes/no field to indicate whether the permit includes a CSO outfall(s). A combined sewer system (CSS) is a wastewater collection system owned by a municipality which conveys sanitary wastewater (domestic, commercial, and industrial) and stormwater through a single pipe system to a publicly owned treatment works. A combined sewer overflow (CSO) is the discharge from a CSS at a point prior to the treatment plant. CSOs are point sources subject to NPDES permit requirements including both technology-based and water quality-based requirements of the Clean Water Act.
Enforcement Information
Last Formal Enforcement Action: The date of the Last Formal Enforcement Action within the selected date range. The date displayed is the date of the most recent milestone event reported in the case record.
Civil Enforcement Case Number: The unique number identifying the civil enforcement action or case.
Federal EPA case numbers follow the format "01-2004-1111", with "01" indicating the appropriate EPA region (or HQ (headquarters), EF (CAA Mobile Source Eastern Field Office), or WF (CAA Mobile Source Western Field Office)), "2004" indicating the fiscal year, and "1111" being a sequential number unique to the case. The fiscal year, in the majority of cases, is the year in which the action was initiated.
State case numbers begin with the state postal abbreviation followed by a hyphen and a sequence number, of up to 17 additional characters or numbers.
For additional detail about civil enforcement cases associated with a facility, see the ECHO Enforcement Case Search and help to search for and view detailed enforcement case reports.
DOJ/Court Docket Number: The docket number assigned by the Department of Justice to EPA's Enforcement Action. This number will identify cases in the Federal Register and in DOJ press releases when a settlement is lodged and entered.
Type Description: The designation of the type of enforcement action. Available types include:
- State CWA Penalty Administrative Order (AO)
- State CWA Non Penalty Administrative Order (AO)
- Emergency Order - Governor
- Order of Suspension or Revocation
- State Administrative Order of Consent
Total Exceedance Counts
The Total Exceedance Counts table presents the total number of DMR exceedances over the selected date range. The chart provides a graphical representation of the counts of DMR exceedances during each monitoring period date.
Note: For a benchmark threshold exceedance to be included in the results, the parameter also needs to be flagged within the database for a percent exceedances calculation. The list of parameters with possible percent exceedance calculations can be downloaded from the Quarterly NNCR Help page (“ICIS-NPDES Parameter Reference Table (CSV)”). Parameters where the PERCENT_EXCEEDENCE_FLAG = N are not included, even if there was a reported exceedance.
Number of Reported DMR Value Exceedances: The total number of DMR exceedances during the date range.
Number of Required DMR Values: The facility's required number of DMR values.
% of Required DMR Values with Exceedances: The percentage of the required DMR values that represent a DMR exceedance violation during the date range. If the percentage is greater than 1%, it is displayed as a rounded integer. If the percentage is between 0-1%, it is displayed to the hundredth of a percent.
Days with Exceedances: The sum of number of days with effluent exceedance for all pollutants, calculated in the Loading Tool based on the duration of the statistical basis. This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
| Statistical Base Type | Days with Exceedances |
|---|---|
| Instant (i.e., contains INST), or no duration specified (e.g., Minimum, Maximum) | 1 |
| Daily (i.e., contains DY) | 1 |
| Weekly (i.e., contains WK) | 7 |
| Monthly (i.e., contains MO) or greater (e.g., quarterly, semiannually, annually) | The number of days in the monitoring period, accounting for the duration of discharge, where reported. See the Loading Tool Technical Users Background Document for more information about duration of discharge. |
Days with Exceedances is the number of days with effluent exceedances in the selected timeframe. Where possible, this is calculated in accordance with the EPA penalty policy or estimated from the permit limit statistical base code descriptions. In instances where the limit time frame is ambiguous, the days in violations for each effluent violation defaults to one. In instances where the permit limit is cumulative, days with effluent exceedances defaults to the total time period. For more information on the EPA penalty policy, please see Interim CWA Settlement Penalty Policy (1995) and the Statistical Base Codes for Days with Exceedances spreadsheet (XLSX) (171 KB).
| No. | Example | Days in Violation Per EPA Policy | Loading Tool "Days with Exceedances" | Differences between EPA Penalty Policy and Loading Tool Calculations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Violation of daily maximum limit for pollutant A, on the 5th of January. | 1 | 1 | The DMR data summarize compliance monitoring data from the entire reporting period (e.g., monthly). For example, the DMR data can indicate that there was a daily max limit exceedance in the reporting period (e.g., daily max violation sometime during the month) but not the exact date (e.g., daily max violation on tenth of the month). |
| 2 | Violation of daily maximum limit for pollutant A, on the 5th, 10th, and 15th of January | 3 | 1 | EPA policy is to count this example as having three Days with Exceedances. ICIS-NPDES only provides one maximum value for the reporting period; therefore, the Loading Tool will only show one maximum exceedance (e.g., the maximum of the daily maximum values), hence, one day with exceedances. |
| 3 | Violation of daily maximum limits for each of pollutants A and B, on the 5th of January. | 2 | 2 | Loading Tool calculation matches EPA policy. |
| 4 | Violation in January of weekly average for pollutant A. | 7 | 7 | Loading Tool calculation matches EPA policy. |
| 5 | Violation in January of monthly average limit for pollutant A. | 31 | 31 | Loading Tool calculation matches EPA policy. |
| 6 | Violation in January of monthly average limit for pollutant A, in which there is evidence that there were no discharges on 4 days (e.g., plant shut down on Sundays). | 27 | 27 | The Loading Tool assumes that discharges occur continuously for the duration of the monitoring period. When Duration of Discharge codes are reported, the Loading Tool adjusts the number of days to reflect the actual number of discharge days per monitoring period. In the case of partial days, the value is rounded to the nearest whole day. See the Technical Users Background Document for more information about duration of discharge. Days with Exceedances accounts for Duration of Discharge codes, when reported. However, there is a limitation with ICIS-NPDES data in that not all NPDES permits require permittees to submit these Duration of Discharge codes when there are intermittent discharges that occur within a monitoring period. Consequently, the tool may overestimate Days with Exceedances for these intermittent dischargers that do not report Duration of Discharge codes. NPDES permittees with intermittent discharges are encouraged to engage with their permit writers to add one of these Duration of Discharge codes to their DMR. NPDES permittees may also contact us if these Duration of Discharge codes are not yet in their DMR. |
| 7 | Violation in January of monthly average limits for both pollutants A and B. | 62 | 62 | Loading Tool calculation matches EPA policy |
| 8 | Violation in January of monthly average limit for pollutant A, and of daily maximum limit for pollutant B on January 5th and 15th. | 33 | 32 | EPA policy is to count the two daily max limit violations for pollutant B as two Days in Violation, but the Loading Tool will only show these daily max limitation violations as one Day with Effluent Exceedance due to the limitations of the DMR data. |
| 9 | Violation in January of monthly average limit for pollutant A, and of daily maximum limit for pollutant A on Jan. 5th and 15th. | 31 | 31 | Loading Tool calculation matches EPA policy. The Loading Tool will not count daily or weekly exceedances if monthly exceedances also occur for the same pollutant, outfall, and monitoring period. |
Months with Exceedances: The number of distinct months in which the NPDES permit had DMR exceedances.
Exceedance Counts by Pollutant
This table provides a summary of the number of effluent limit exceedances by pollutant. Sort data by clicking on the column header in the table.
Note: For a benchmark threshold exceedance to be included in the results, the parameter also needs to be flagged within the database for a percent exceedances calculation. The list of parameters with possible percent exceedance calculations can be downloaded from the Quarterly NNCR Help page (“ICIS-NPDES Parameter Reference Table (CSV)”). Parameters where the PERCENT_EXCEEDENCE_FLAG = N are not included, even if there was a reported exceedance.
Parameter Code: A five-character code in ICIS-NPDES that identifies the regulated pollutant parameter in a NPDES permit and specifies both the pollutant name and pollutant form (e.g., dissolved or suspended). Multiple parameters can apply to a single pollutant or CAS number. The parameter code is hyperlinked to its associated effluent charts.
Description: The name of the parameter.
Statistical Base Type: The unit of measure applicable to the limit and DMR values.
Contains Potential Outliers?: An indication that data has been flagged as containing potential outliers or data errors. To identify and report a potential data error to EPA, see Error Corrections.
Number of Reported DMR Value Exceedances: The number of DMR exceedances violations.
Number of Required DMR Values: The facility's required number of DMR values.
% of Required DMR Values with Exceedances: The percentage of the required DMR values that represent a DMR exceedance violation during the date range. If the percentage is greater than 1%, it is displayed as a rounded integer. If the percentage is between 0-1%, it is displayed to the hundredth of a percent.
Days with Exceedances: The number of days with effluent exceedances, calculated in the Loading Tool based on the statistical base type. Days with Exceedances is calculated in accordance with EPA Penalty Policy, with some exceptions. This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
| Statistical Base Type | Days with Exceedances |
|---|---|
| Instant (i.e., contains INST), or no duration specified (e.g., Minimum, Maximum) | 1 |
| Daily (i.e., contains DY) | 1 |
| Weekly (i.e., contains WK) | 7 |
| Monthly (i.e., contains MO) or greater (e.g., quarterly, semiannually, annually) | The number of days in the monitoring period, accounting for the duration of discharge, where reported. See the Loading Tool Technical Users Background Document for more information about duration of discharge. |
Exceedance Details
This table provides a record of each effluent limit exceedance within the selected data range. Sort data by clicking on the column header in the table. Use the customize columns dropdown to select the data most important to you. All available columns are displayed by default.
Note: For a benchmark threshold exceedance to be included in the results, the parameter also needs to be flagged within the database for a percent exceedances calculation. The list of parameters with possible percent exceedance calculations can be downloaded from the Quarterly NNCR Help page (“ICIS-NPDES Parameter Reference Table (CSV)”). Parameters where the PERCENT_EXCEEDENCE_FLAG = N are not included, even if there was a reported exceedance.
Date: The monitoring period end date.
Outfall-Limit Set: The 3-digit code for the permitted feature where the discharge occurs, followed by the unique identifier for the limit set, generated in ICIS-NPDES.
Parameter: The parameter code and description.
Average Daily Flow (MGD): The average daily flow for the outfall, in units of Million Gallons per Day (MGD). This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
Statistical Base Type: The unit of measure applicable to the limit and DMR values.
DMR Value: The measured value of the parameter. Where applicable, a qualifier may also display (e.g., <, <=, >, or >=) to indicate that the reported value is an upper or lower bound, respectively, on the true value. "E" indicates an estimated value.
Benchmark Threshold: The permitted limit for the parameter.
% Exceedance: The percent that the DMR value exceeds the benchmark threshold.
Load over Threshold (lb/period): The calculated load (pounds) over the permit limit. See Hierarchy of Loading Calculations in the Water Pollutant Loading Tool for more information. This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
Load over Threshold (lb-eq/period): The toxic weighted pound equivalent (TWPE) value over the threshold, calculated by multiplying the load over threshold by the pollutant toxic weighting factor (TWF). This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
Note that loadings may not be calculated for all DMR measurements. The Loading Tool can only calculate mass discharges for pollutants that are measured either as mass quantities or concentrations. Therefore some pollutants, such as pathogen indicators, temperature, pH, and toxicity parameters measured as percent are displayed without calculated loadings. Further, the Loading Tool cannot calculate a load for concentration measurements if a wastewater flow measurement is not provided.
Days per Period: The number of days in the monitoring period. For monthly monitoring periods the Loading Tools uses the number of days in the specific month. Seven days is displayed for weekly monitoring periods.
Days with Exceedances: The number of days with effluent exceedances, calculated in the Loading Tool based on the statistical base type. Days with Exceedances is calculated in accordance with EPA Penalty Policy, with some exceptions. This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
Note that if there is more than one exceedance for one parameter at the same outfall during a monitoring period (e.g., exceeding both an average and maximum statistical base type), the Loading Tool will only calculate days with exceedances for one of the exceedance records, to avoid double counting. This display is only available for the effluent limit exceedances view of the report.
| Statistical Base Type | Days with Exceedances |
|---|---|
| Instant (i.e., contains INST), or no duration specified (e.g., Minimum, Maximum) | 1 |
| Daily (i.e., contains DY) | 1 |
| Weekly (i.e., contains WK) | 7 |
| Monthly (i.e., contains MO) or greater (e.g., quarterly, semiannually, annually) | The number of days in the monitoring period, accounting for the duration of discharge, where reported. See the Loading Tool Technical Users Background Document for more information about duration of discharge. |
